Display a barplot with a gap (missing range) on one axis
gap.barplot.RdDisplays a barplot with a missing range.
Usage
gap.barplot(y,gap,xaxlab,xtics,yaxlab,ytics,xlim=NA,ylim=NA,xlab=NULL,
ylab=NULL,horiz=FALSE,col,...)Arguments
- y
a vector of data values
- gap
the range of values to be left out
- xaxlab
labels for the x axis ticks
- xtics
position of the x axis ticks
- yaxlab
labels for the y axis ticks
- ytics
position of the y axis ticks
- xlim
Optional x limits for the plot
- ylim
optional y limits for the plot
- xlab
label for the x axis
- ylab
label for the y axis
- horiz
whether to have vertical or horizontal bars
- col
color(s) in which to plot the values
- ...
arguments passed to barplot.
Details
Displays a barplot omitting a range of values on the X or Y axis. Typically used when there is a relatively large gap in the range of values represented as bar heights. See axis.break for a brief discussion of plotting on discontinuous coordinates.
If the user does not ask for specific y limits, the function will calculate limits based on the range of the data values. If passing specific limits, remember to subtract the gap from the upper limit.
Examples
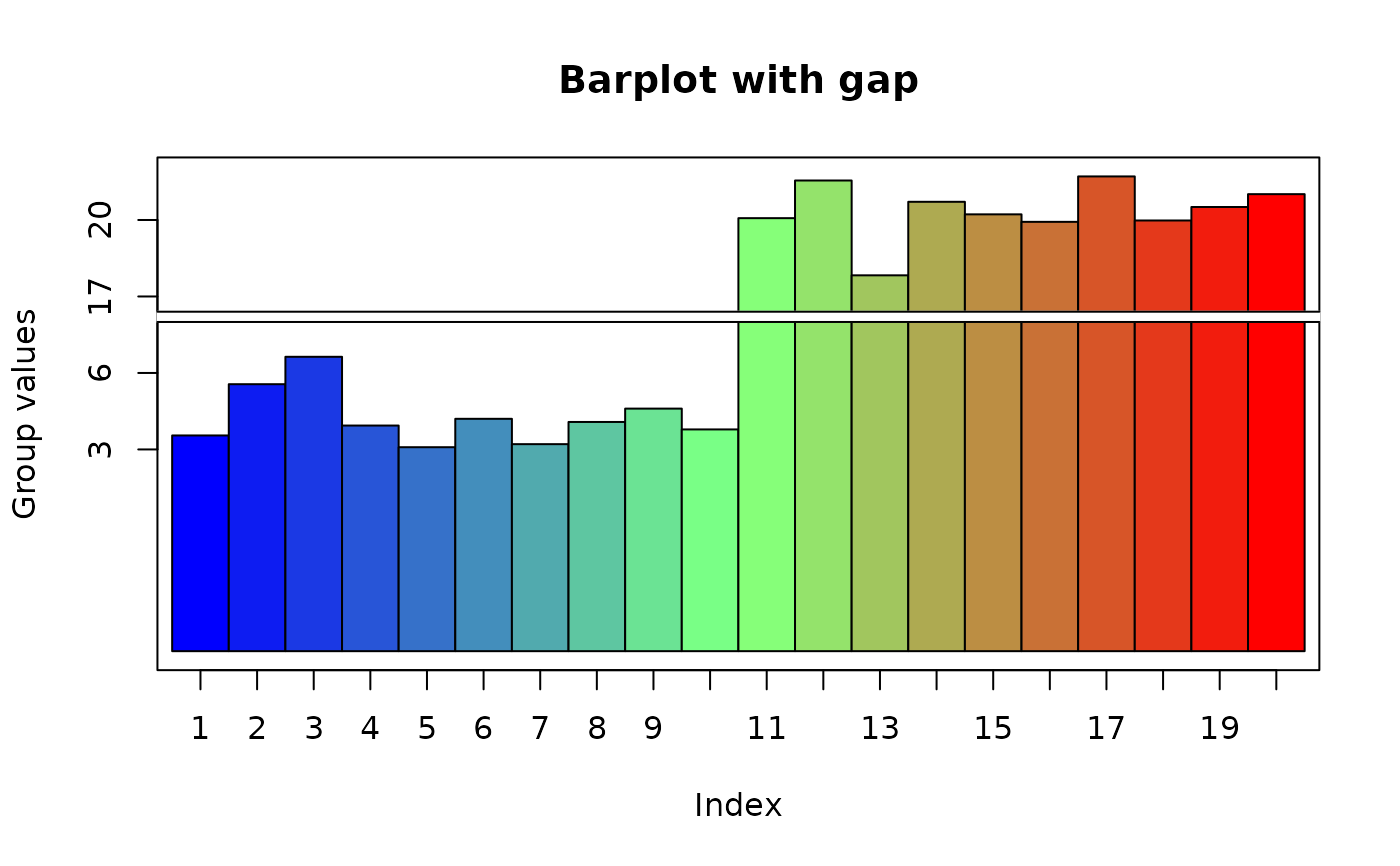
twogrp<-c(rnorm(10)+4,rnorm(10)+20)
gap.barplot(twogrp,gap=c(8,16),xlab="Index",ytics=c(3,6,17,20),
ylab="Group values",main="Barplot with gap")
#> ylim -5.174695 13.64423
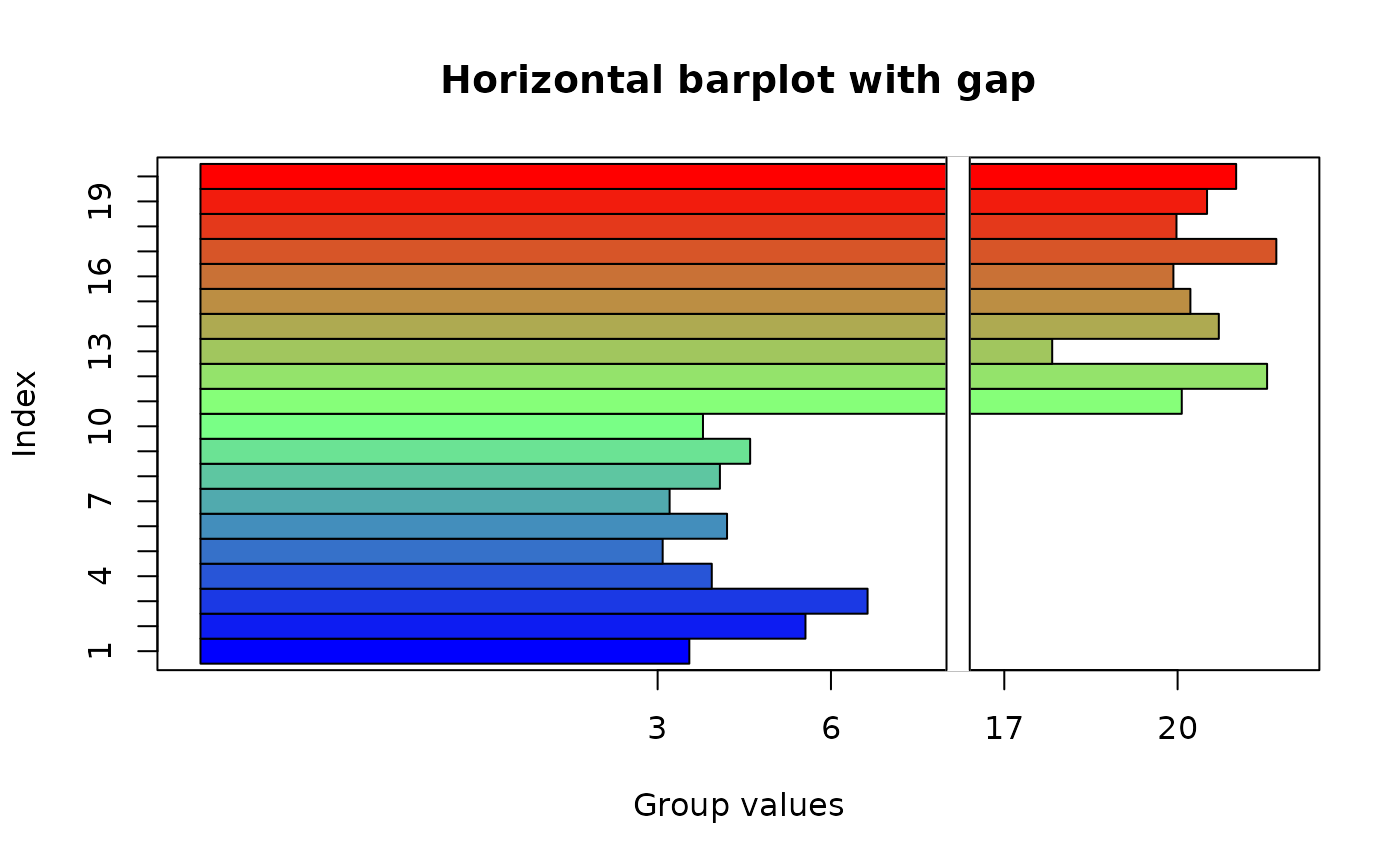
 gap.barplot(twogrp,gap=c(8,16),xlab="Index",ytics=c(3,6,17,20),
ylab="Group values",horiz=TRUE,main="Horizontal barplot with gap")
#> ylim -5.174695 13.64423
gap.barplot(twogrp,gap=c(8,16),xlab="Index",ytics=c(3,6,17,20),
ylab="Group values",horiz=TRUE,main="Horizontal barplot with gap")
#> ylim -5.174695 13.64423