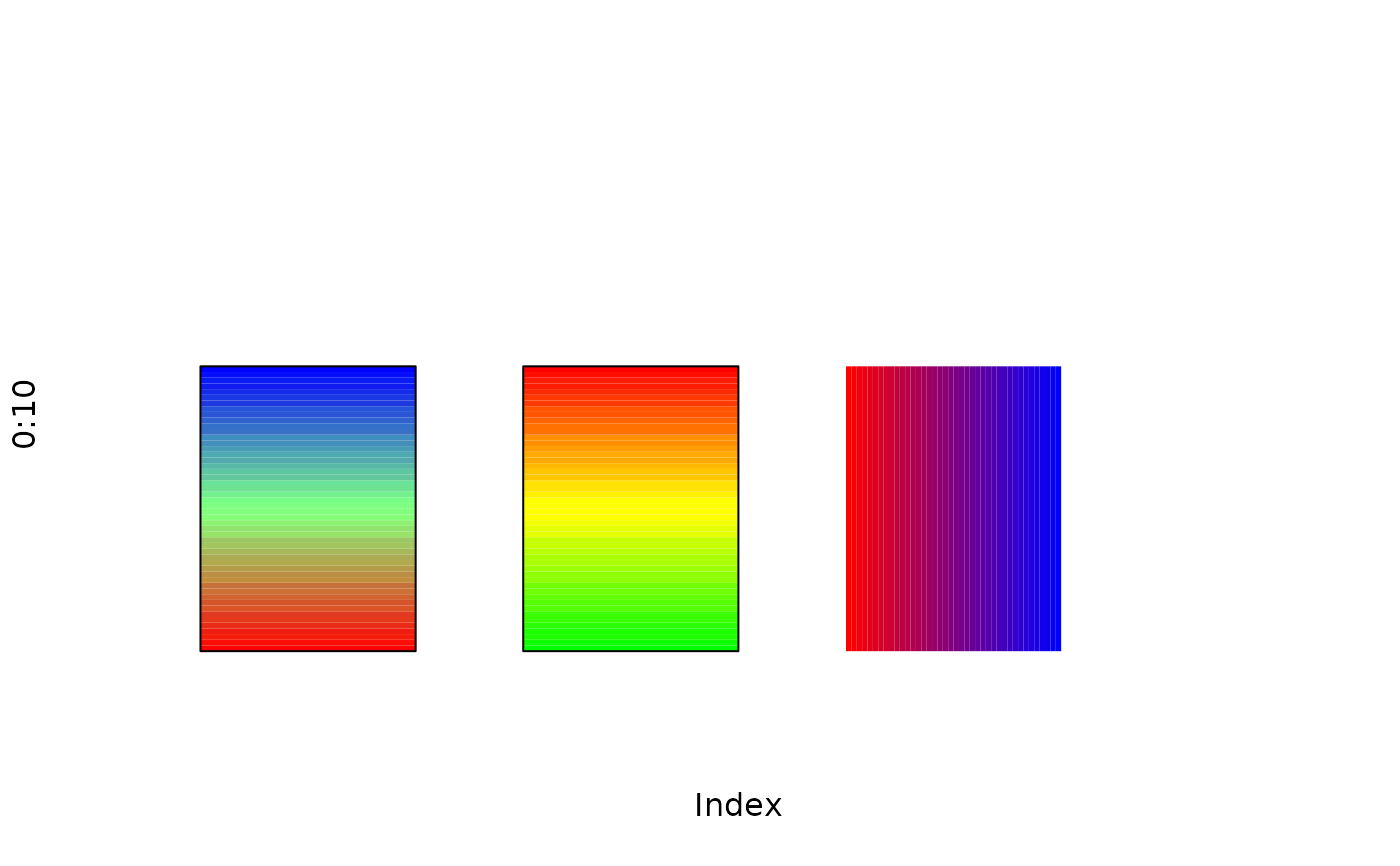Display a rectangle filled with an arbitrary color gradient
gradient.rect.Rdgradient.rect draws a rectangle consisting of nslices subrectangles of the colors in col or those returned by color.gradient if col is NULL. The rectangle is 'sliced' in the direction specified by gradient.
Usage
gradient.rect(xleft,ybottom,xright,ytop,reds,greens,blues,col=NULL,
nslices=50,gradient="x",border=par("fg"))Arguments
- xleft,ybottom,xright,ytop
Positions of the relevant corners of the desired rectangle, as in rect.
- reds,greens,blues
vectors of the values of the color components either as 0 to 1 or ,if any value is greater than 1, 0 to 255.
- col
Vector of colors. If supplied, this takes precedence over reds, greens, blues and nslices will be set to its length.
- nslices
The number of sub-rectangles that will be drawn.
- gradient
whether the gradient should be horizontal (x) or vertical.
- border
The color of the border around the rectangle (NA for none).
Examples
# get an empty box
plot(0:10,type="n",axes=FALSE)
# run across the three primaries
gradient.rect(1,0,3,6,reds=c(1,0),
greens=c(seq(0,1,length=10),seq(1,0,length=10)),
blues=c(0,1),gradient="y")
# now a "danger gradient"
gradient.rect(4,0,6,6,c(seq(0,1,length=10),rep(1,10)),
c(rep(1,10),seq(1,0,length=10)),c(0,0),gradient="y")
# now just a smooth gradient across the bar
gradient.rect(7,0,9,6,col=smoothColors("red",38,"blue"),border=NA)